Différences entre les versions de « Aide mémoire d'Arthur pour l'utilisation de Git »
toross>WikiAdmin |
m (1 version importée) |
||
| (2 versions intermédiaires par 2 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 60 : | Ligne 60 : | ||
== Configuration == | == Configuration == | ||
=== Hosts === | |||
{{parW|1= | |||
{{m|{{mm|/etc/hosts}}}} n'est pas utilisé mais c'est {{m|{{mm|/c/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts}} }} qui est utilisé. | |||
{{code|lang=hosts|code= | |||
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp. | |||
# | |||
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. | |||
# | |||
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each | |||
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should | |||
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. | |||
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one | |||
# space. | |||
# | |||
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual | |||
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol. | |||
# | |||
# For example: | |||
# | |||
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server | |||
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host | |||
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself. | |||
# 127.0.0.1 localhost | |||
# ::1 localhost | |||
192.168.20.108 hdedibox3 | |||
192.168.20.100 compaqmini | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
=== L'essentiel === | |||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
*{{mm|git config}} | *{{mm|git config}} | ||
| Ligne 71 : | Ligne 101 : | ||
:: ⟼ {{mm|<locGitNameRep>/.git/config}} | :: ⟼ {{mm|<locGitNameRep>/.git/config}} | ||
::Seuelement pour la base locale (quand on est dans <locGitNameRep>) | ::Seuelement pour la base locale (quand on est dans <locGitNameRep>) | ||
Voir ses paramètres : | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config --list | |||
}} | }} | ||
=== system === | ou | ||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config core.autocrlf | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
=== system : {{m|1=/etc/git…}} === | |||
==== Certificat auto-certifié ==== | ==== Certificat auto-certifié ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
| Ligne 85 : | Ligne 124 : | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
}} | }} | ||
=== global === | ==== Editer le contenu de la configuration au niveau du system ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config --system --edit # /etc/gitconfig | |||
}} | |||
ce qui peut donner sous windows à ({{mm|/etc/gitconfig}}) : | |||
{{code|lang=cfg|code= | |||
[diff "astextplain"] | |||
textconv = astextplain | |||
[filter "lfs"] | |||
clean = git-lfs clean -- %f | |||
smudge = git-lfs smudge -- %f | |||
process = git-lfs filter-process | |||
required = true | |||
[http] | |||
sslBackend = openssl | |||
sslCAInfo = C:/pf/git/mingw64/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt | |||
sslVerify = false | |||
[core] | |||
fscache = false | |||
symlinks = false | |||
[pull] | |||
rebase = true | |||
[credential] | |||
helper = manager-core | |||
[credential "https://dev.azure.com"] | |||
useHttpPath = true | |||
[init] | |||
defaultBranch = master | |||
}} | |||
old: | |||
{{code|lang=cfg|code= | |||
[diff "astextplain"] | |||
textconv = astextplain | |||
[filter "lfs"] | |||
clean = git-lfs clean -- %f | |||
smudge = git-lfs smudge -- %f | |||
process = git-lfs filter-process | |||
required = true | |||
[http] | |||
sslBackend = openssl | |||
sslCAInfo = C:/pf/git/mingw64/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt | |||
sslVerify = false | |||
[core] | |||
autocrlf = true | |||
fscache = true | |||
symlinks = false | |||
[pull] | |||
rebase = true | |||
[credential] | |||
helper = manager-core | |||
[credential "https://dev.azure.com"] | |||
useHttpPath = true | |||
[init] | |||
defaultBranch = master | |||
[diff] | |||
tool = diff -Bb | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
=== global : {{m|1=~/.git…}} === | |||
==== Identification de l'utilisateur ==== | ==== Identification de l'utilisateur ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
| Ligne 95 : | Ligne 194 : | ||
==== Exemple de fichier config ==== | ==== Exemple de fichier config ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config --edit --global # ~/.gitconfig | |||
}} | |||
{{code|lang=ini|code= | |||
[http] | |||
sslVerify = false | |||
[user] | |||
name = Arthur Torossian | |||
email = arthur.torossian@edf.fr | |||
[credential "https://at.bht.fr"] | |||
provider = generic | |||
[credential "http://pac-ad-edf.proxy.edf.fr:3131"] | |||
provider = generic | |||
[credential "https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr"] | |||
provider = generic | |||
[core] | |||
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global | |||
excludesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitignore_global | |||
ignorecase = true | |||
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global | |||
whitespace = trailing-space,-space-before-tab,indent-with-non-tab,cr-at-eol | |||
blank-at-eof = false | |||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
Old: | |||
{{code|lang=ini|code= | |||
[http] | [http] | ||
sslVerify = false | sslVerify = false | ||
| Ligne 116 : | Ligne 237 : | ||
ignorecase = true | ignorecase = true | ||
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global | attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global | ||
whitespace = cr-at-eol | whitespace = trailing-space,-space-before-tab,indent-with-non-tab,cr-at-eol | ||
blank-at-eof = false | blank-at-eof = false | ||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
==== Las attributs .gitattributes ==== | ==== Las attributs .gitattributes - fin de ligne CR LF CRLF LFCR line endings ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
Pour régler les problèmes d'espace, de tabulation ou de code de fin de ligne des fichiers textes il faut ajouter la configuration des attributs des formats des fichiers (voir ci-après) et configurer les deux variables suivantes localement comme ici ou globalement : | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config core.eol lf | |||
git config core.autocrlf input | |||
}} | |||
{{CadreR|1=Si des fichiers sont marqués modifiés pour les problèmes d'espaces et de fin de lignes alors il | |||
faut les ajouter et commiter, après quoi le bonne configuration se mettront en place : | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git add -u | |||
git commit -m "nomralisation eof whitespace" | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
voir : | |||
* [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9976986/force-lf-eol-in-git-repo-and-working-copy Force LF eol in git repo and working copy] | |||
* [https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2 Pro Git book 2nd Edition (2014)] | |||
* [https://docs.github.com/fr/get-started/getting-started-with-git/configuring-git-to-handle-line-endings#refreshing-a-repository-after-changing-line-endings Configuration de Git pour traiter les fins de ligne] | |||
* [https://git-scm.com/docs/gitattributes gitattributes] | |||
* [https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Customizing-Git-Git-Attributes 8.2 Customizing Git - Git Attributes] | |||
On peut le configurer en global ou en local {{mm|.gitattributes}} crée à la racine en le versionnant dans la base même si l'on veut le retrouver sur d'autres machines. | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | {{code|lang=bash|code= | ||
git config --global core.attributesfile ~/.gitattributes_global | git config --global core.attributesfile ~/.gitattributes_global | ||
}} | }} | ||
Contenus possible : | |||
{{code|lang=text|code= | {{code|lang=text|code= | ||
* text=auto | |||
*.bat text eol=crlf whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2 | |||
*.csv text | |||
*.doc -text diff | |||
*.docx -text diff | |||
*.html text | |||
*.idx -text diff | |||
*.ini text | |||
*.jpg -text diff | |||
*.mov -text diff | |||
*.mp4 -text diff | |||
*.pack -text diff | |||
*.pdf -text diff | |||
*.png -text diff | |||
*.ppt -text diff | |||
*.pptx -text diff | |||
*.py text eol=lf whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2 diff=python | |||
*.pyc -text diff | |||
*.sample -text diff | |||
*.sh text whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2 diff=bash | |||
*.svg text | |||
*.tx text | |||
*.txt text | |||
*.uml -text diff | |||
*.xls -text diff | |||
*.xlsm -text diff | |||
*.xlsx -text diff | |||
*.xml text | |||
}} | }} | ||
voir(old) [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1510798/trying-to-fix-line-endings-with-git-filter-branch-but-having-no-luck/1511273#1511273 Trying to fix line-endings] | |||
}} | }} | ||
==== Ignorer les fichiers .gitignore ==== | ==== Ignorer les fichiers .gitignore ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
| Ligne 158 : | Ligne 330 : | ||
tmp* | tmp* | ||
gen* | gen* | ||
old* | |||
external* | external* | ||
*generated* | *generated* | ||
| Ligne 180 : | Ligne 353 : | ||
*.so | *.so | ||
*.pyc | *.pyc | ||
__pycache__ | |||
# Packages # | # Packages # | ||
############ | ############ | ||
| Ligne 210 : | Ligne 383 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Rq|Ne pas laisser d'espace devant les pattern de filtrage.}} | {{Rq|Ne pas laisser d'espace devant les pattern de filtrage.}} | ||
=== Local : {{m|1=.git/config}} === | |||
{{parW|1= | |||
{{code|code=bash|code= | |||
git config --edit # .git/config | |||
}} | |||
{{code|code=in|code= | |||
[core] | |||
repositoryformatversion = 0 | |||
filemode = false | |||
bare = false | |||
logallrefupdates = true | |||
symlinks = false | |||
[remote "old-origin"] | |||
url = https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.colmat.git | |||
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/old-origin/* | |||
[gui] | |||
wmstate = zoomed | |||
geometry = 893x435+208+208 418 464 | |||
[submodule "modAtTool"] | |||
active = true | |||
url = https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.git | |||
[remote "at64g"] | |||
url = F:/base/gitDvlp/ciclope.git/ | |||
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/at64g/* | |||
[remote "origin"] | |||
url = https://gitlab.pleiade.edf.fr/ciclope/ciclope-code.git | |||
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/* | |||
[branch "master"] | |||
remote = origin | |||
merge = refs/heads/master | |||
[http] | |||
sslVerify = false | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
=== La complétion des commandes de git === | === La complétion des commandes de git === | ||
| Ligne 227 : | Ligne 435 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
=== Les outils : éditeur et fusion et différence === | === Les outils : éditeur et fusion et différence (diff tool merge tool meld tkdiff) === | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
{{cadre|1= | |||
Pour travailler sous windows et linux sans les problèmes de fin de ligne \lf \cr il suffit de positionner {{mm|core.autocrlf}} sur {{mm|input}} [https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Customizing-Git-Git-Configuration source]: | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git config --global core.autocrlf input | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
<source lang="bash"> | <source lang="bash"> | ||
git config --global core.editor gedit | git config --global core.editor gedit | ||
| Ligne 331 : | Ligne 545 : | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
<source lang="bash"> | <source lang="bash"> | ||
git config --list | git config --list --show-origin | ||
git config user.name | git config user.name | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Ligne 456 : | Ligne 670 : | ||
git clone <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep> | git clone <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Cette commande créera la répertoire < | Cette commande créera la répertoire <locGitNameRep>. | ||
}} | |||
==== Cloner une branche ou un tag particulier ==== | |||
{{parW|1= | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
# pour une branche | |||
git clone -b <branchName> <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep> | |||
# ou pour un tag | |||
git clone -b <tagName> <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep> | |||
}} | |||
Cette commande créera la répertoire <locGitNameRep>. | |||
}} | }} | ||
=== Pour une base locale existante modifier l'emplacement du répertoire {{dq|.git}} === | === Pour une base locale existante modifier l'emplacement du répertoire {{dq|.git}} === | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
| Ligne 1 033 : | Ligne 1 258 : | ||
==== Voir l'historique - git-log ==== | ==== Voir l'historique - git-log ==== | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
La doc en ligne : https://git-scm.com/docs/git-log | * La doc en ligne : [https://git-scm.com/docs/git-log] | ||
D'un fichier donné: | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | |||
git log --pretty=format:"%h %cd %Cgreen%s %Cred%d" \ | |||
--graph --abbrev-commit --date="format:%Y/%m/%d %Hh%M" \ | |||
--follow ciclopeM3z.py | |||
}} | |||
Globalement: | |||
{{code|lang=bash|code= | {{code|lang=bash|code= | ||
# court | # court | ||
| Ligne 1 322 : | Ligne 1 554 : | ||
* Les commandes GIT que vous devez absolument connaître ! | * Les commandes GIT que vous devez absolument connaître ! | ||
*: https://www.hostinger.fr/tutoriels/commandes-git/ | *: https://www.hostinger.fr/tutoriels/commandes-git/ | ||
* Gloassary - Git commands | |||
*: https://www.atlassian.com/git/glossary | |||
* git-cheatsheet | * git-cheatsheet | ||
*: http://ndpsoftware.com/git-cheatsheet.html | *: http://ndpsoftware.com/git-cheatsheet.html | ||
| Ligne 1 362 : | Ligne 1 596 : | ||
*: [http://mercurial.selenic.com/wiki/GitConcepts mercurial.selenic.com] | *: [http://mercurial.selenic.com/wiki/GitConcepts mercurial.selenic.com] | ||
}} | }} | ||
=== Clients === | === Clients === | ||
{{parW|1= | {{parW|1= | ||
Version actuelle datée du 26 décembre 2023 à 11:26
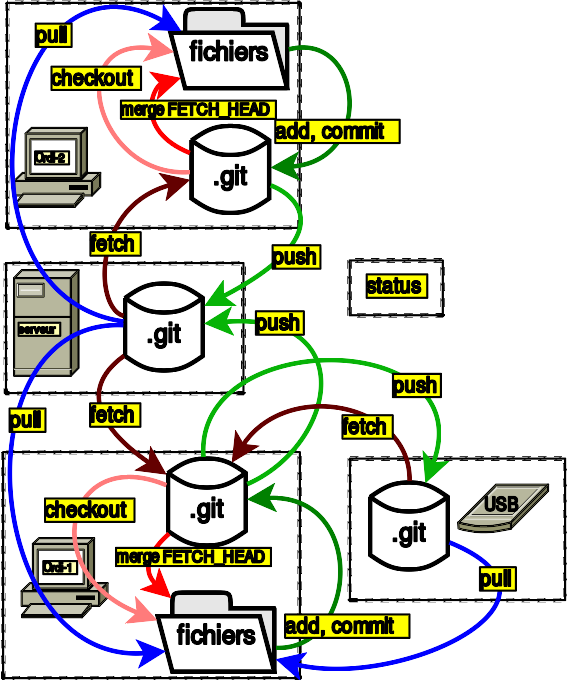
1 L'essentiel
2 Las variables
- <rem…> remote
- distant, une base git distante, sur une autre machine
- <loc…> local
- local, une base git locale, sur la machine utilisée
- <dep…> depository
- depository (repository ne sera pas utilisé pour ne pas confondre avec repertoire)
- <wrk…> work
- work, de travail, ce qui correspond en général au répertoire de travail
- <…Url> url
- uniform resource locator, adresse web d'une base git
- <…Dir> <…Rep> directory
- répertoire physique sur le disque dur.
- <…ParentDir> <…ParentRep> parent directory
- répertoire parent sur le disque dur.
- <…GitName…>
- nom de la base git
Exemples de <remGitNameUrl> :
atoross@claumep1:/home/var/git/loco file:///home/atoross/dvlp/gitTests/remGitBase https://anomnymous@git.salome-platform.org/gitpub/modules/med.git
3 Les différentes espaces de Git
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
3.1 stash
L'espace stash (stash) (cachette) est une espace de stockage temporaire des données qui ne sont pas encore enregistrées (not commited); c'est une sauvegarde de l'espace staging area.
3.2 staging area - index
3.3 working directory
3.4 local depository
3.5 remote depository
4 Configuration
4.1 Hosts
/etc/hosts n'est pas utilisé mais c'est /c/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts qui est utilisé.
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
192.168.20.108 hdedibox3
192.168.20.100 compaqmini4.2 L'essentiel
- git config
- --system
- ⟼ /etc/gitconfig
- Pour tous les utilisateurs
- --global
- ⟼ ~/.gitconfig
- Pour l'utilsateur courant
- ⟼ <locGitNameRep>/.git/config
- Seuelement pour la base locale (quand on est dans <locGitNameRep>)
Voir ses paramètres :
git config --list
ou
git config core.autocrlf
4.3 system : /etc/git…
4.3.1 Certificat auto-certifié
Solution 1 :
su -
git config --system http.sslVerify false
Solution 2 :
export GIT_SSL_NO_VERIFY=true
4.3.2 Editer le contenu de la configuration au niveau du system
git config --system --edit # /etc/gitconfig
ce qui peut donner sous windows à (/etc/gitconfig) :
[diff "astextplain"]
textconv = astextplain
[filter "lfs"]
clean = git-lfs clean -- %f
smudge = git-lfs smudge -- %f
process = git-lfs filter-process
required = true
[http]
sslBackend = openssl
sslCAInfo = C:/pf/git/mingw64/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt
sslVerify = false
[core]
fscache = false
symlinks = false
[pull]
rebase = true
[credential]
helper = manager-core
[credential "https://dev.azure.com"]
useHttpPath = true
[init]
defaultBranch = master
old:
[diff "astextplain"]
textconv = astextplain
[filter "lfs"]
clean = git-lfs clean -- %f
smudge = git-lfs smudge -- %f
process = git-lfs filter-process
required = true
[http]
sslBackend = openssl
sslCAInfo = C:/pf/git/mingw64/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt
sslVerify = false
[core]
autocrlf = true
fscache = true
symlinks = false
[pull]
rebase = true
[credential]
helper = manager-core
[credential "https://dev.azure.com"]
useHttpPath = true
[init]
defaultBranch = master
[diff]
tool = diff -Bb
4.4 global : ~/.git…
4.4.1 Identification de l'utilisateur
git config --global user.name "Arthur TOROSSIAN"
git config --global user.email "arthur.torossian@edf.fr"
4.4.2 Exemple de fichier config
git config --edit --global # ~/.gitconfig
[http]
sslVerify = false
[user]
name = Arthur Torossian
email = arthur.torossian@edf.fr
[credential "https://at.bht.fr"]
provider = generic
[credential "http://pac-ad-edf.proxy.edf.fr:3131"]
provider = generic
[credential "https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr"]
provider = generic
[core]
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global
excludesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitignore_global
ignorecase = true
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global
whitespace = trailing-space,-space-before-tab,indent-with-non-tab,cr-at-eol
blank-at-eof = false
Old:
[http]
sslVerify = false
[user]
name = Arthur Torossian
email = arthur.torossian@edf.fr
[credential "https://at.bht.fr"]
provider = generic
[credential "http://pac-ad-edf.proxy.edf.fr:3131"]
provider = generic
[credential "https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr"]
provider = generic
[core]
excludesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitignore_global
ignorecase = true
attributesfile = C:/Users/C07138/.gitattributes_global
whitespace = trailing-space,-space-before-tab,indent-with-non-tab,cr-at-eol
blank-at-eof = false
4.4.3 Las attributs .gitattributes - fin de ligne CR LF CRLF LFCR line endings
Pour régler les problèmes d'espace, de tabulation ou de code de fin de ligne des fichiers textes il faut ajouter la configuration des attributs des formats des fichiers (voir ci-après) et configurer les deux variables suivantes localement comme ici ou globalement :
git config core.eol lf
git config core.autocrlf input
Si des fichiers sont marqués modifiés pour les problèmes d'espaces et de fin de lignes alors il faut les ajouter et commiter, après quoi le bonne configuration se mettront en place :
git add -u
git commit -m "nomralisation eof whitespace"
voir :
- Force LF eol in git repo and working copy
- Pro Git book 2nd Edition (2014)
- Configuration de Git pour traiter les fins de ligne
- gitattributes
- 8.2 Customizing Git - Git Attributes
On peut le configurer en global ou en local .gitattributes crée à la racine en le versionnant dans la base même si l'on veut le retrouver sur d'autres machines.
git config --global core.attributesfile ~/.gitattributes_global
Contenus possible :
* text=auto
*.bat text eol=crlf whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2
*.csv text
*.doc -text diff
*.docx -text diff
*.html text
*.idx -text diff
*.ini text
*.jpg -text diff
*.mov -text diff
*.mp4 -text diff
*.pack -text diff
*.pdf -text diff
*.png -text diff
*.ppt -text diff
*.pptx -text diff
*.py text eol=lf whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2 diff=python
*.pyc -text diff
*.sample -text diff
*.sh text whitespace=blank-at-eol,-blank-at-eof,-space-before-tab,tab-in-indent,tabwidth=2 diff=bash
*.svg text
*.tx text
*.txt text
*.uml -text diff
*.xls -text diff
*.xlsm -text diff
*.xlsx -text diff
*.xml text
4.4.4 Ignorer les fichiers .gitignore
Ajouter le ~/.gitignore_global aux fichiers exclus en tapant, y compris sous WINDOWS:
git config --global core.excludesfile ~/.gitignore_global
Rendre la configuration non sensible à la casse :
git config --global core.ignorecase true
cette option se retrouve alors dans le fichier wrkDir/.git/config Pour un répertoire spécifique, créer ce fichier nommé .gitignore dans le répertoire à filtrer (en général la racine qui est wrkDir) en le complétant par :
.gitignore
.project
.pydevproject
.settings
noPull
noPush
*chenal3.cfg*
modAtTool
# My generated #
###################
tmp*
gen*
old*
external*
*generated*
*Copie*
*Copy*
*.puml
*PlantUml.png
# Editor generted #
###################
*~
*bak
*back.py
# Compiled source #
###################
*.com
*.class
*.dll
*.exe
*.o
*.so
*.pyc
__pycache__
# Packages #
############
# it's better to unpack these files and commit the raw source
# git has its own built in compression methods
*.7z
*.dmg
*.gz
*.iso
*.jar
*.rar
*.tar
*.zip
# Logs and databases #
######################
*.log
# OS generated files #
######################
.DS_Store
.DS_Store?
._*
.Spotlight-V100
.Trashes
ehthumbs.db
Thumbs.db
Ne pas laisser d'espace devant les pattern de filtrage.
4.5 Local : .git/config
git config --edit # .git/config
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = false
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
symlinks = false
[remote "old-origin"]
url = https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.colmat.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/old-origin/*
[gui]
wmstate = zoomed
geometry = 893x435+208+208 418 464
[submodule "modAtTool"]
active = true
url = https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.git
[remote "at64g"]
url = F:/base/gitDvlp/ciclope.git/
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/at64g/*
[remote "origin"]
url = https://gitlab.pleiade.edf.fr/ciclope/ciclope-code.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/master
[http]
sslVerify = false
4.6 La complétion des commandes de git
Copier le fichier de complétion:
cp /etc/bash_completion.d/git ~/.git-completion.sh
et ajouter dans ~/.bashrc la ligne suivante :
source ~/.git-completion.sh
4.7 Un prompt affichant les branches
4.8 Les outils : éditeur et fusion et différence (diff tool merge tool meld tkdiff)
Pour travailler sous windows et linux sans les problèmes de fin de ligne \lf \cr il suffit de positionner core.autocrlf sur input source:
git config --global core.autocrlf input
git config --global core.editor gedit
git config --global merge.tool tkdiff
git config --global diff.tool meld
git config --global difftool.meld.path "/usr/bin/meld"
git config --global difftool.prompt false
git config --global merge.tool meld
git config --global mergetool.meld.path "/usr/bin/meld"
git config --global mergetool.prompt false
Utilisation
git difftool HEAD^1 comMultiZone/common.py
4.9 Dimensionner la taille des paquets d'envoi quand le protocole http est utilisé
SI le massage suivant est ertourné :
Expected ok/error, helper said 2004[...]
git config --global http.postBuffer 209715200
4.10 Le fichier bashrc pour git bash sous windows
Se trouve dans C:\Users\<your user name>.
Si on exécute la commande echo ~ on obtient par exemple « /c/Users/Arthur »4.11 Les alias
Lire d'abord Exemple de référence
alias gad='git add '
..
git config --global alias.sw 'checkout'
git config --global alias.ad 'add'
git config --global alias.br 'branch'
git config --global alias.cm 'commit' -m
git config --global alias.co 'checkout'
git config --global alias.cur 'symbolic-ref --short HEAD'
git config --global alias.lg 'log --pretty=format:"[%h][%cN]%Cgreen[%s]%Cred[%d]" --date=iso --graph --abbrev-commit'
git config --global alias.ltag 'describe --exact-match --abbrev=0'
git config --global alias.pl 'pull'
git config --global alias.pu 'push'
git config --global alias.slg 'log --pretty=format:"[%h]%Cgreen[%s]%Cred[%d]" --graph --abbrev-commit'
git config --global alias.st 'status'
git config --global alias.sw 'checkout'
git config --global alias.rv ' remote -v '
git config --global alias.ra 'remote add '
git config --global alias.me 'merge --no-ff --no-commit'
Dautres alias plus spécifiques
alias branch-merge-point = !bash -c 'diff --old-line-format=--new-line-format= <(git rev-list --first-parent \"${1:-master}\") <(git rev-list --first-parent \"${2:-HEAD}\")
git config -l |grep alias
alias.le=log --oneline --decorate
alias.filelog=log -u
alias.fl=log -u
alias.dl=!git ll -1
alias.dlc=diff --cached HEAD^
alias.dr=!f() { git diff $1^..$1; }; f
alias.lc=!f() { git ll $1^..$1; }; f
alias.diffr=!f() { git diff $1^..$1; }; f
alias.f=!git ls-files | grep -i
alias.grep=grep -Ii
alias.gr=grep -Ii
alias.cp=cherry-pick
alias.st=status -s
alias.cl=clone
alias.ci=commit
alias.co=checkout
alias.br=branch
alias.diff=diff --word-diff
alias.dc=diff --cached
alias.r=reset
alias.r1=reset HEAD^
alias.r2=reset HEAD^^
alias.rh=reset --hard
alias.rh1=reset HEAD^ --hard
alias.rh2=reset HEAD^^ --hard
4.12 Vérifier la configuration
git config --list --show-origin
git config user.name
5 Aide
git <commande> -h
man git-<commande>
git help <commande>
git --help <commande>
exemple :
git config -h
man git-config
git help config
git --help config
6 Les commandes les plus utilisées
cp : copier(copy)
mv : déplacer(mv)
rec : enregistrer(record), inscrire juste le nom
unrec : dés-enregistrer(unrecord), effacer le nom
6.1 Désigner une révision - HEAD
- HEAD désigne la dernière révision, notée N, de la branche pointée par le locRep.
- HEAD~ ou HEAD^ ou HEAD~1 HEAD^1 désigne la révision N-1.
- HEAD~2 désigne la révision N-2.
- HEAD^2 désigne la révision N-2 du deuxième parent dans le cas où on peut avoir plusieurs parents.
- ORIG_HEAD est l'état antérieur de HEAD pour certaines opérations critiques. Il est moins utile maintenant que git a reflog: git reflog show donne par exemple :
febdfb9 (HEAD -> master, origin/master, origin/HEAD) HEAD@{0}: checkout: moving from at to master 010837a (origin/at, at) HEAD@{1}: checkout: moving from master to at febdfb9 (HEAD -> master, origin/master, origin/HEAD) HEAD@{2}: commit: save 010837a (origin/at, at) HEAD@{3}: pull: Fast-forward
Les révisions sont aussi appelées des « commit ». Par exemple HEAD^1 désigne le dernier « commit » (last commit). Dans la documention de git les « commit » sont noté « <commit> ».
exemples :
git lg HEAD~1^2
git lg origin/master~1
git log --pretty=format:"%h" --graph
* 1bd1d09
|\
| * 37d48e9
| |\
| | * edae2b9
| | * 42bb57e
| |/
|/|
| * 74dc61f
| * c43c75d
|/
* eedbf2e
* 0361888
* 87c79ea
git lg -1 HEAD~1
* eedbf2e
git lg -1 HEAD^1
* eedbf2e
git lg -1 HEAD~2
* 0361888
git lg -1 HEAD^2
37d48e9
6.2 S'authentifier aévec mot de passe stocké temporairement
Pour garder le mot de passe pour 3 heures
git config --global credential.helper 'cache --timeout=10800'
Pour garder le mot de passe pour une heure
git config --global credential.helper 'cache --timeout=3600'
Pour garder le mot de passe pour un certain temps
git config --global credential.helper cache
Sous windows (pas possible de mettre un timeout):
git config --global credential.helper wincred
Si vous êtes bloqué sous windows, on peut gérer les dientifications en cherchant dans tapant « Gérer vos informations d'identification »
Attention dans certain cas par défaut le paramétrage peut être dans --system.
6.3 Copier une base locale - clone
git clone <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep>
6.3.1 Cloner une branche ou un tag particulier
# pour une branche
git clone -b <branchName> <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep>
# ou pour un tag
git clone -b <tagName> <remGitNameUrl> <locGitNameRep>
6.4 Pour une base locale existante modifier l'emplacement du répertoire « .git »
Utilisation de « --separate-git-dir »
git clone <remGitNameRep> <locGitNameRep> \
--separate-git-dir=<newPathOfLocGitRep>
Exemple :
git clone /c/chenal3/chenal /c/chenal3/newChenal \
--separate-git-dir=/c/chenal3/newChenalGitRep
6.5 Ajouter/Add un fichier au «stgArea»
git add <filepath>
git add <dirpath>
git add ./rep1/dvlp1File.txt
Seulement les éléments déjà ajoutés:
git add -u [--] [filepattern ...]
git add -u
git add -u "*.c" "../*.h"
Tous les éléments:
git add -A [--] [filepattern ...]
git add -A
git add -A "*.c" "../*.h"
Attention git add -A supprimera dans stgArea les fichiers qui ne sont plus dans wrkDir. Attention git add -n permet de tester sans toucher stgArea, très pratique si l'on n'est pas sûr, exemple git add -n -A "../ser*" "../inter*".
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
└────rec──────▶│
"add" ou "add -u"
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
└────rec──────▶│
some
└unrec─▶∅
"add -A"
6.6 Montrer les différences et comparer
Entre deux tags :
git diff tag1 tag2
git diff tag1 tag2 -- some/file/name
Pour ne voir que la liste des fichiers qui comportent des différences:
git diff tag1 tag2 --stat
Pour une différence avec le répertoire courant:
git diff tagX
git diff tagX -- some/file/name
git diff tagX --stat
6.7 Enregistrer/Commiter les fichiers déjà ajoutés dans «locDep»
git commit -m <message>
git commit -m "dvlp01-01"
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
│ └unrec─▶∅
└───────────cp───────────▶<newSha1>
<sha1>
...
"commit -m <message>"
6.8 Annuler
6.8.1 Annuler un ajout d'un fichier au «stgArea» - “unadd” - "reset <path>"
git reset <filepath>
git reset HEAD <filepath>
« wrkDir » n'est pas impacté.
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
∅◀─unrec─┘
"reset <path>"
6.8.2 Annuler/Uncommiter le dernier enregistrement dans « locDep »
git reset --soft HEAD^
« wrkDir » et « stgArea » ne sont pas impactés.
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
∅◀─mv─<HEAD>
<HEAD^>
...
"reset --soft HEAD^"
La commande git reset --soft HEAD ne fait rien
6.8.3 Annuler/Uncommits plusieurs enregistrements dans « locDep »
git reset --soft HEAD^^^
git reset --soft dba146f
« wrkDir » et « stgArea » ne sont pas impactés.
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
∅◀─mv─ <HEAD>
∅◀─mv─ <HEAD^>
∅◀─mv─ <HEAD^^>
<HEAD^^^>=<Commit>
...
"reset --soft <Commit>"
6.8.4 Annuler/unLocalyModify toutes les modifications dans « wrkDir »
git reset --hard
git reset --hard HEAD
« wrkDir » et « stgArea » sont directement impactés.
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
│ ∅◀─unrec─┘
│◀───────────cp────────<HEAD>
...
"reset --hard HEAD"
6.8.5 Annuler/unLocalyModify les modifications d'un fichier dans « wrkDir »
git checkout HEAD Makefile
stash wrkDir stgArea locDep remDep
│ ∅◀─unrec─┘
│◀───────────cp────────<HEAD>
...
"git checkout HEAD Makefile"
6.9 Dépôt distant
6.9.1 Changer le dépôt distant « origin »
git remote rename origin origin-old
git remote add origin git@gitlab.pleiade.edf.fr:eelCounter/eelCounter.git
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/master master
6.9.2 Connaître l'url de la base distante - remote
git remote -v
origin <remGitNameUrl> (fetch)
origin <remGitNameUrl> (push)
6.9.3 Ajouter un dépôt distant - remote add
remoteName est nom (une variable) correspondant à la base distante
git remote add <remoteName> <path>
git remote add <remoteName> <remotePath>
git remote add <remoteName> <localPath>
git remote add <remoteName> <url>
cas distant :
git remote add claumep1 http://claumep1.der.edf.fr/git/P112N_pivot.git
git remote add atorossClaui2v9 ssh://atoross@claui2v9.der.edf.fr/local01/atoross/dvlp/vishnu/github_vishnu.git
git pull <remoteName> [<remoteBranchName>]
git pull atorossClaui2v9 zmq
cas local:
git remote add theTrunk /home/C07138/opentelemacTrunk
git remote -v
git branch
git stash
git pull theTrunk master
git pull theTrunk master
git branch gouttedo
git branch
git checkout gouttedo
git pull theTrunk gouttedo
6.9.4 Enlever un dépôt distant - remote rm
git remote rm claui2v6
6.9.5 Inspecter un dépôt distant - remote -v show
git remote -v show <remoteName>
Example :
git remote -v show origin
6.10 Merger
6.10.1 Merger une branche (locale) dans la branche courante
git merge multiZoneDvlp
6.10.2 Merger seulement des fichiers d'une branche dans la branche courante
git merge --no-ff --no-commit <branch>
git status
git merge --no-ff --no-commit at
git status
- --no-ff : pas de fast-forward
- --no-commit : pas de commit
Vous aurez alors une liste de fichiers automatiquement fusionnés(merged) et d'autres avec des fusions comportant des conflits.
Pour les fichiers auto-fusionnés on peut inspecter le fusion avec la commande :
git diff --cached <filepath>
Pour fusions avec conflit il faut les éditer et faire le choix soi-même, sinon on peut choisir entre la branche et la branche courante.
Choix de la branche courante :
git checkout HEAD <filepath>
Choix de la branche à fusionner :
git checkout <branch> <filepath>
6.10.3 Merger une branche distante - branch merge
git checkout master
git branch -a -v
git merge remotes/origin/BOU/addStudyExamples
6.10.4 gérer les conflits lors des merges/fusions
Le cas imprévu :
git pull lex256 master
git checkout --theirs facture/facture.ods
git add -facture/facture.ods
git pull lex256
Le cas prévisible :
git pull -s ours
git pull -X theirs
6.11 Branches
6.11.1 Supprimer une branche
exemple :
git branch -d sph_rpa-1.0.0.0
git branch -D sph_rpa-1.0.0.0 # sans confirmation
6.11.2 Lister les branches - fetch, branch
exemple :
git fetch -p
git branch -a -v
6.11.3 Récupérer / changer une branche distante - fetch, checkout --track
git fetch <remoteName>
git checkout --track <remoteName>/<remoteBrancheName>
- checkout : http://git-scm.com/docs/git-checkout
exemple :
git fetch -p
git branch -a -v
git checkout remotes/origin/BOU/addStudyExamples
6.11.4 Créer une nouvelle branche - branch
git branch <newBranchName> <refBranchName>
git branch v0.1 master
git checkout v0.1
git push origin at/v0.1
6.11.5 Partager une nouvelle branche - push <remoteName> <xx>/<topic>
git branch <xx>/<topic>
git co <xx>/<topic>
git branch
...
git push <remoteName> <xx>/<topic>
6.11.6 Renomer une branche - git branch -m <new-name>
6.11.6.1 Rename your local branch
If you are on the branch you want to rename:
git branch -m new-name
If you are on a different branch:
git branch -m old-name new-name
6.11.6.2 Delete the old-name remote branch and push the new-name local branch
git push origin :old-name new-name
6.11.6.3 Reset the upstream branch for the new-name local branch
git push origin -u new-name
6.12 Tag
6.12.1 Taguer une version d'application (pushable)
git tag -a cloggingGridModel_rpa-1.0.0 -m "cloggingGridModel version rpa-1.0.0"
6.12.2 Le dernier commit - tag -s -a v0.1 -m "FPL 0.1"
Préparer une clé gpg
gpg --gen-key
gpg --list-keys
Real name: Arthur Torossian
Email address: arthur.torossian@edf.fr
You selected this USER-ID:
"Arthur Torossian <arthur.torossian@edf.fr>"
/home/atoross/.gnupg/pubring.gpg
--------------------------------
pub 3072D/DDDFB557 2013-07-05
uid Arthur Torossian <arthur.torossian@edf.fr>
sub 3072g/999BED15 2013-07-05
Il faut créer de tag avec annotation sinon le tag est lightweight dans ce cas c'est juste un pointeur sur le nœud du commit.
git tag -s -a v0.1 -m "FPL 0.1"
git tag -v v0.1
git show v0.1
6.12.3 Un ancien commit - tag -s -a v0.1 -m "FPL 0.1" 979e98c
git tag -s -a "ciclope.py_x5-1.2.0.1" -m "ciclope.py version x5-1.2.0.1" 979e98c
6.12.4 Lister les tags sans notations (lightweight tags, annotated tags)
git for-each-ref refs/tags/ --format '%(objecttype) %(refname:short)'
6.12.5 Un ancien commit - tag -s -a v0.1 9fceb02
git tag -s -a v0.1 9fceb02
6.12.6 Partager les tags - push origin v0.1
git push origin v0.1
ou
git push origin --tags
6.12.7 Supprimer un tag local
git tag -d alpha-3.0.0.0
6.12.8 Supprimer un tag distant
git push --delete origin alpha-3.0.0.0
6.13 Chercher (find) un mot/expression dans un fichier dans toutes les versions
git rev-list --all
6.14 Supprimer
6.14.1 Supprimer un répertoire - rm -r fuelCell
git rm -r fuelCell
git rm -r lightModel airportsTraffic
6.14.2 Supprimer un répertoire / fichier dans toute l'historique - git filter-branch -f --tree-filter
git filter-branch -f --tree-filter "rm -rf ./donnees/studyExamples " --prune-empty -- --all
git push --force
6.15 Sous base ou module
6.15.1 Organisation
6.15.2 Ajouter un sous module - une autre base git dans un sous répertoire
git submodule add https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.git modAtTool
Il faut tout de suite configurer la liaison avec une branche par exemple ici ciclope. Ainsi chaque utilisateur du module a sa propre version.
git config -f .gitmodules submodule.modAtTool.branch ciclope
6.15.3 Configurer la branche du sous module
git config -f .gitmodules submodule.modAtTool.branch ciclope
more .gitmodules
[submodule "modAtTool"]
path = modAtTool
url = https://git.forge.pleiade.edf.fr/git/verona.git
branch = ciclope
6.15.4 Récuprer un sous module - puller un sous module
La première fois :
git submodule update --init --recursive
Après on peut utiliser la commande pull lui-même :
git pull --recurse-submodules
6.15.5 Changer l'url du sous module
git config --file=.gitmodules submodule.modAtTool.url ../modAtTool
git config --file=.gitmodules submodule.modAtTool.branch chenal3
git submodule sync
git submodule update --init --recursive --remote
6.15.6 Renommer un sous module
git mv modAtTool/ modExtTool
gcm "rename extern tool"
6.15.7 Supprimer un sous module
git rm modExtTool
gcm "delete extern tool"
6.15.8 Cloner une base avec les sous modules
Pour une version ≥ 2.13 :
git clone --recurse-submodules https://...myBase.git myBase
6.15.9 Voir l'historique - git-log
- La doc en ligne : [1]
D'un fichier donné:
git log --pretty=format:"%h %cd %Cgreen%s %Cred%d" \
--graph --abbrev-commit --date="format:%Y/%m/%d %Hh%M" \
--follow ciclopeM3z.py
Globalement:
# court
git log --pretty=format:"%h %cd %Cgreen%s %Cred%d" --graph --abbrev-commit --date="format:%Y/%m/%d %Hh%M"
# long
$git log --pretty=format:"%h %cd %cn %Cgreen%s %Cred%d" --graph --abbrev-commit --date="format:%Y/%m/%d %Hh%M"
7 Comment s'organiser
7.1 Créer une nouvelle base
cd <locGitBaseRep>
git init
touch README
git add README
git commit -m "init"
git branch
7.2 Exporter ou archiver hors base - archive
git archive --format=tar HEAD ./pivotLanguage/ | gzip > test.tar.gz
7.3 Créer un dépôt commun
Sur le serveur distant:
mkdir <remGitBaseRep>
cd <remGitBaseRep>
git init --bare
git update-server-info
cd ..
chown -R www-data:atoross <remGitBaseRep>
Sur l'une des machines de travail ou base de travail:
git clone https://claumep1.der.edf.fr/git/hydro myHydro
git br
La commande git br ne renvoie aucune branche. Il faut au minimum ajouter(add) un fichier et enregistrer l'ajout (commit) afin que la branche par défaut master apparaisse :
git add conv.py
git cm -m "test python file reading med file" conv.py
git br
Cette fois-ci nous avons bien la branche master :
* master
Je ne sais toujours pas pourquoi il faut ajouter absolument un fichier pour que la branche master puisse exister localement !
Attention tout n'est pas fini
Si on utilise https/http, pour pusher il faut ajouter son login dans .git/config sinon le push ne passe pas !
[remote "origin"]
url = https://atoross@at.bht.fr/git/atTools.git
Finallement on peut pusher :
git push --set-upstream origin master
Pour pouvoir « pusher » et « puller » il faut également ajouter au moins un fichier :
git add readme.txt
gcm "init"
git push
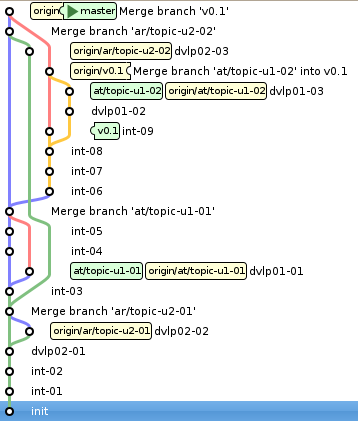
7.4 Le rôle de l'intégrateur
cd integratorLocGitBase/
evim intFile.txt
git add intFile.txt
git cm -m "int-01"
git lg origin/master
git push
git lg origin/master
git add intFile.txt
git cm -m "int-02"
git push
git lg origin/master
git fetch
git co --track origin/ar/topic-u2-01
git co master
git branch
git merge ar/topic-u2-01
#git merge --log --no-ff ar/topic-u2-01
git push
git co ar/topic-u2-01
git pull
more dvlp2File.txt
git co master
git merge --log --no-ff ar/topic-u2-01
git push
git config user.name "Integrator"
git config --list
git status
more intFile.txt
git add intFile.txt
git commit -m "int-03"
git push
git lg origin/master
git remote show origin
git lg
git st
git add intFile.txt
git cm -m "int-04"
git push
git lg
git add intFile.txt
git cm -m "int-05"
git push
git lg
git fetch origin
git co --track origin/at/topic-u1-01
git br
git status
git br
git sw master
git br
git merge --log --no-ff at/topic-u1-01
git status
git push
git slg
7.5 Rôle de l'utilisateur 1
cd dvlp1GitBase/
git lg origin/master
git pull
branch at/topic-u1-01
git sw at/topic-u1-01
git branch
git add dvlp1File.txt
git status
git cm -m "dvlp01-01"
git lg
branch
push origin at/topic-u1-01
git co master
7.6 Rôle de l'utilisateur 2
git clone file:///home/atoross/dvlp/gitTests/remGitBase dvlp2GitBase
cd dvlp2GitBase/
git br ar/topicu2-01
git sw ar/topicu2-01
git br
git config user.name "Arturo Torossiani"
git pull
git lg
git branch ar/topic-u2-01
git branch
git checkout ar/topic-u2-01
git branch
git cm -am "dvlp02-01"
git add dvlp2File.txt
git cm -am "dvlp02-01"
git push origin ar/topic-u2-01
git branch
git cm -am "dvlp02-02"
git push origin ar/topic-u2-01
git lg
more dvlp2File.txt
git slg
7.6.1 Créer un patch
8 git-svn
9 Mes bases Git
10 Git servi par apache
10.1 Créer une base sans les fichiers locaux - Create a bare repository
- bare
- nue, sans la partie de travail
cd <remGitNameRep>
git init --bare
git update-server-info
ou à partir d'une base existante
cd <remGitNameParentRep>
git clone --bare <remGitNameUrl> <GitName>.git
git update-server-info
10.2 Configurer apache
on peut ajouter un fichier git :
################################################################################
# git
################################################################################
Alias /git/ "/local01/www/arth/git/"
<Location /git>
DAV on
Options -Indexes
<RequireAll>
Require all granted
SSLRequireSSL
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Git"
AuthBasicProvider file
AuthUserFile "/etc/apache2/passwd/passwords_admin"
<RequireAll>
Require valid-user
</RequireAll>
</RequireAll>
</Location>
a2ensite git
a2enmod dav
a2enmod dav_fs
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Pour terminer il faut lire Créer une base commune distante
11 Problèmes rencontrés
11.1 Manque de mémoire
remote: Counting objects: 11191, done.
remote: warning: suboptimal pack - out of memory
remote: fatal: Out of memory, malloc failed (tried to allocate 348936731 bytes)
remote: aborting due to possible repository corruption on the remote side.
fatal: protocol error: bad pack header
12 Liens
12.1 Rsync avec git bash sous windows
- Voir RSync
12.2 Autres
- Les commandes GIT que vous devez absolument connaître !
- Gloassary - Git commands
- git-cheatsheet
- svn basic commands to git commands
- La dernière version de mon .bash-scm est disponible sur le dépot Git suivant:
- $ git clone http://repo.or.cz/r/git-scripts.git
- Enfin, le dépôt sima utilisé pour la démo ainsi que le script de la démo sont récupérable ici si vous voulez expérimenter.
- $ git clone git://cln46mr/home/git/sima
- Main Web Site - Site officiel
- commandes
- Référence rapide
- Référence
- Community Book
- Livre Pro Git - Scott Chacon - Apress
- Tutoriel officiel
- Autres tutoriels
- Manuel officiel
- Pour les scientifiques http://eagain.net/articles/git-for-computer-scientists/
- Les commandes http://schacon.github.com/git/everyday.html
- 8 ways to share your git repository
- Setting up GIT with Apache Smart HTTP/S and LDAP
- Topic branches
- A successful Git branching model
- Mercurial for Git users
12.3 Clients
- gitk
- le projet : http://gitk.sourceforge.net/
- la doc : http://git-scm.com/docs/gitk
- Smart Git (smartgit)
12.4 Serveur web
- How To Install A Public Git Repository On A Debian Server
- How to setup Git server on Linux Container in Debian